

Aukua and Garland Technology have joined forces to combat the villainous issues connected with network latency!
Garland’s Superpower: Supersonic Duplication
Aukua’s Superpower: Telepathic Monitoring
Their mission: To secure your network while weakening latency.
In their recent joint solution, Aukua and Garland not only attack impending critical network concerns but also inspect vulnerabilities within the traditional approach to latency. To break down the solution, the video highlights the vigilant questions you need to answer when constructing your network infrastructure and how these partners address them.
Like the relationship of Captain America and Falcon - separate, the two are strong, but together they fight the toughest black hats. The two play off each other’s strengths, by leveraging Garland TAPs to extract live network data and Aukua’s monitors to analyze packets or malicious activity.|
With less than 3ns latency added, Aukua’s MGA2510 Latency Monitoring Analyzer reads the data supplied by passive out-of-band Network TAPs. The 100% visibility from Garland’s TAPs enables the Aukua solution to fully monitor and directly analyze network application traffic without introducing packets into the network.
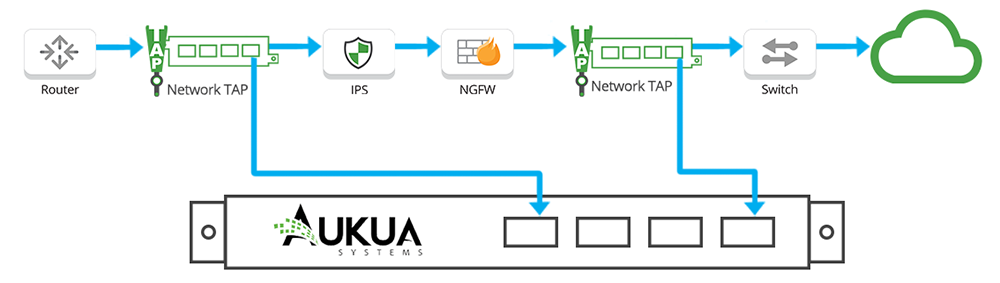
Garland’s unwavering traffic aggregation, load balancing, and filtering provides users with full control over traffic behavior and flexibility for aggregation and regeneration. The dynamic, yet simple use case grabs real-time stats and graphical analysis from Aukua’s analyzers to strengthen a powerful and customizable set of L2-L7 filters and triggers.
Aukua’s MGA2510 is the only Ethernet test platform to provide inline visibility with a focus on capture, analysis, and monitoring large throughput networks. They build, deploy, and support the network infrastructure, measuring one-way latency experienced by production traffic with 1.0ns precision.
When network latency is the enemy, Aukua and Garland Technology have unearthed their kryptonite. For more information about this dynamic duo, check out their joint solution here!
If the inline security tool goes off-line, the TAP will bypass the tool and automatically keep the link flowing. The Bypass TAP does this by sending heartbeat packets to the inline security tool. As long as the inline security tool is on-line, the heartbeat packets will be returned to the TAP, and the link traffic will continue to flow through the inline security tool.
If the heartbeat packets are not returned to the TAP (indicating that the inline security tool has gone off-line), the TAP will automatically 'bypass' the inline security tool and keep the link traffic flowing. The TAP also removes the heartbeat packets before sending the network traffic back onto the critical link.
While the TAP is in bypass mode, it continues to send heartbeat packets out to the inline security tool so that once the tool is back on-line, it will begin returning the heartbeat packets back to the TAP indicating that the tool is ready to go back to work. The TAP will then direct the network traffic back through the inline security tool along with the heartbeat packets placing the tool back inline.
Some of you may have noticed a flaw in the logic behind this solution! You say, “What if the TAP should fail because it is also in-line? Then the link will also fail!” The TAP would now be considered a point of failure. That is a good catch – but in our blog on Bypass vs. Failsafe, I explained that if a TAP were to fail or lose power, it must provide failsafe protection to the link it is attached to. So our network TAP will go into Failsafe mode keeping the link flowing.
Single point of failure: a risk to an IT network if one part of the system brings down a larger part of the entire system.
Heartbeat packet: a soft detection technology that monitors the health of inline appliances. Read the heartbeat packet blog here.
Critical link: the connection between two or more network devices or appliances that if the connection fails then the network is disrupted.